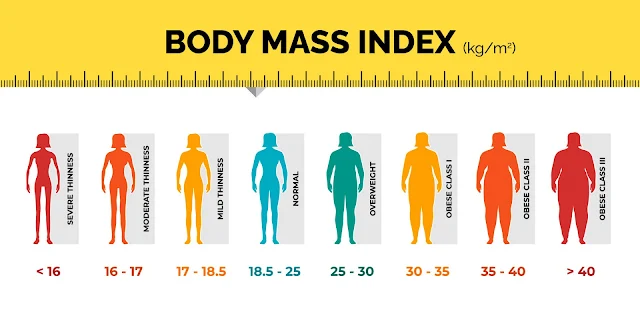
Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide to Healthy and Sustainable Weight Loss
Introduction
Weight loss is a common goal for many people, driven by the desire to improve health, boost self-confidence, and enhance physical appearance. While losing weight can be beneficial for overall well-being, it is essential to approach it with a focus on sustainability and health. This article will explore the fundamentals of weight loss, effective strategies, and common myths, ensuring you have the tools to achieve your goals safely.
Understanding Weight Loss
At its core, weight loss occurs when you consume fewer calories than you burn, creating a caloric deficit. However, healthy and long-term weight loss involves much more than simply cutting calories. It includes a balanced approach to nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle changes that can be maintained over time.
Key Components of Healthy Weight Loss
Balanced Nutrition
Caloric Deficit: To lose weight, you need to create a calorie deficit, meaning you consume fewer calories than your body needs to maintain its current weight. This can be done by eating less, exercising more, or a combination of both.
Macronutrients: Focus on a balanced intake of macronutrients—proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Each plays an essential role in weight management:
- Protein: Supports muscle repair and can help you feel full longer. Lean meats, legumes, and tofu are good sources.
- Carbohydrates: Opt for complex carbs like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to fuel your body with energy.
- Fats: Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are important for hormone function and satiety.
Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating, even when eating healthy foods.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps regulate metabolism, manage hunger, and supports overall health.
Regular Exercise
Cardio Exercises: Activities like walking, running, cycling, or swimming help burn calories and improve heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
Strength Training: Building muscle through resistance training (weight lifting, bodyweight exercises) helps increase your metabolism, as muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, even at rest.
Flexibility and Balance: Activities such as yoga or Pilates improve flexibility, balance, and mental focus, which can be beneficial for overall fitness.
Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Sleep deprivation can negatively affect hunger hormones, leading to increased appetite and poor food choices.
Stress Management: High stress can lead to emotional eating and weight gain. Incorporate stress-relief techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or hobbies you enjoy.
Consistency Over Perfection: Focus on small, manageable changes that you can stick with in the long run, rather than drastic diets or workout routines that are unsustainable.
Popular Weight Loss Strategies
Calorie Counting
Counting calories can help you understand how much you're consuming and ensure you maintain a caloric deficit. Apps and online tools can simplify this process. However, the focus should still be on nutrient-dense foods rather than just low-calorie options.
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. Common approaches include the 16:8 method (16 hours of fasting, 8-hour eating window) or 5:2 method (eating normally for five days, reducing calorie intake on two non-consecutive days). This strategy can help reduce overall calorie intake and improve metabolism.
Diets such as Keto, Paleo, or general low-carb approaches focus on reducing carbohydrates, often replacing them with higher fat and protein intake. These diets may be effective for short-term weight loss, but long-term adherence is important for sustained results.
Plant-Based Diets
Vegetarian or vegan diets, which emphasize plant-based foods like vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains, are naturally lower in calories and high in nutrients. These diets can promote weight loss when done with a focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
Common Myths About Weight Loss
Myth: You need to starve yourself to lose weight.
Reality: Extreme calorie restriction can slow down your metabolism, lead to muscle loss, and make it harder to maintain weight loss. It’s better to aim for a moderate caloric deficit that allows for steady, sustainable progress.
Myth: All calories are the same.
Reality: The quality of the calories you consume matters. 100 calories from a donut affect your body differently than 100 calories from vegetables. Focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide vitamins, minerals, and energy for optimal health.
Myth: Carbs make you gain weight.
Reality: Carbs themselves don’t cause weight gain, but eating too many processed or simple carbohydrates can. Complex carbs like whole grains and vegetables are an important part of a balanced diet.
Myth: You can target fat loss in specific areas.
Reality: Spot reduction is a myth. While you can strengthen specific muscle groups, fat loss occurs evenly across the body, depending on genetics and overall caloric deficit.
Tracking Progress
Scale Weight: Weighing yourself regularly can give insight into your progress. However, it’s essential not to rely solely on the scale as muscle gain, water retention, and hormonal fluctuations can cause short-term changes.
Measurements: Track your body measurements (waist, hips, chest, arms) to see physical changes over time.
Clothing Fit: Often, changes in how your clothes fit can be a better indicator of fat loss than the number on the scale.
Non-Scale Victories: Pay attention to improvements in energy levels, stamina, mood, and overall health. These can be significant indicators of progress, even if the scale isn’t moving as quickly as you'd like.
Tips for Long-Term Success
- Set Realistic Goals: Aim to lose 1-2 pounds per week, which is considered a healthy and sustainable rate of weight loss.
- Create a Routine: Make exercise and healthy eating a part of your daily routine rather than short-term solutions.
- Stay Accountable: Keep track of your progress with a journal or app, and consider joining a support group or finding an accountability partner.
- Be Patient: Weight loss is a gradual process. Stay focused on long-term health rather than immediate results.
Conclusion
Weight loss is more than just a numbers game—it’s about developing healthy, sustainable habits that improve your overall well-being. A combination of balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes will help you reach your weight loss goals and maintain them long-term. Always consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine to ensure that your approach is safe and effective.
weight loss, sustainable weight loss, healthy weight loss, weight loss tips, weight loss strategies, intermittent fasting, calorie counting, low-carb diets, plant-based diet, weight loss myths, caloric deficit